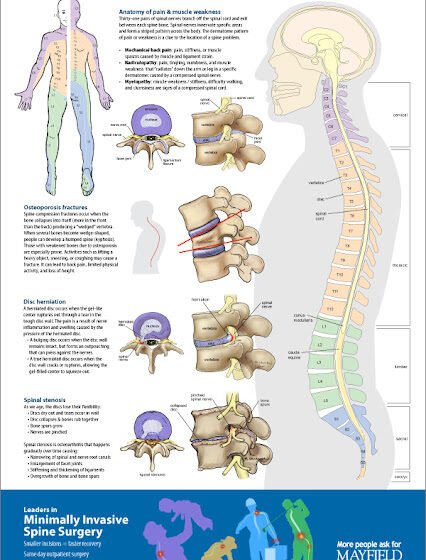
Spinal wounds and conditions can altogether affect an individual’s quality of life. The spine, composed of vertebrae, plates, nerves, and muscles, plays a significant part in supporting the body and encouraging development. This article investigates different sorts of spine wounds and conditions, their causes, side effects, determination, treatment alternatives, and preventive measures.

Anatomy of the Spine
The human spine comprises of 33 vertebrae partitioned into five regions:
Cervical Spine (Neck): Comprising seven vertebrae (C1-C7), it underpins the head and permits for a wide extend of motion. Thoracic Spine (Upper Back): Made up of twelve vertebrae (T1-T12), it interfaces to the ribs and secures imperative organs.
Lumbar Spine (Lower Back): Comprising of five vertebrae (L1-L5), it bears much of the body’s weight and permits for flexibility. Sacral Spine: Shaped by five melded vertebrae, it interfaces the spine to the pelvis.
Coccygeal Spine: Comprising four intertwined vertebrae, this locale shapes the tailbone. Common Spine Injuries Spinal wounds can happen due to injury, monotonous push, or degenerative conditions.
Here are a few common types:
Herniated Disc: A herniated circle happens when the delicate inward gel of a spinal circle projects through a tear in the external layer. This can compress adjacent nerves, driving to torment, deadness, or shortcoming in the arms or legs.
Causes: Age-related degeneration Heavy Lifting Sudden turning movements Symptoms: Pain emanating down an arm or leg Numbness or tingling Muscle weakness Spinal Fractures Fractures in the vertebrae can result from traumatic wounds such as falls or car mishaps. Osteoporosis can too lead to compression fractures.
Symptoms: Severe back pain Deformity (slouched back) Difficulty moving
Spinal Stenosis
This condition includes narrowing of the spinal canal, which can put weight on the spinal rope and nerves.
Causes:
Age-related changes
Arthritis
Herniated discs
Symptoms:
Pain in the lower back or neck
Numbness or shivering in limbs
Difficulty walking
Spondylolisthesis
This happens when one vertebra slips forward over another, frequently causing nerve compression.
Causes:
Degenerative changes
Birth defects
Stress fractures
Symptoms:
Lower back pain
Muscle tightness
Sciatica
Common Neck Injuries
Neck wounds regularly emerge from injury or destitute pose.
Here are a few predominant neck conditions:
Whiplash: Whiplash is a neck harm coming about from sudden twitching developments, commonly seen in car accidents.
Symptoms:
Neck torment and stiffness
Headaches
Dizziness
Cervical Radiculopathy
This condition happens when a nerve in the neck is compressed or aggravated, driving to torment that transmits into the bear or arm.
Symptoms:
Sharp torment in the neck
Numbness or shivering in arms
Weakness in hold strength
Diagnosis of Spine Injuries
Diagnosing spine wounds regularly includes a combination of therapeutic history survey.
Physical examination, and imaging tests:
Medical History: Understanding side effects and any past injuries.
Evaluating run of movement and neurological function.
Imaging Tests:
X-rays: To check for breaks or misalignments.
MRI: Gives nitty gritty pictures of delicate tissues like circles and nerves.
CT looks: Offers cross-sectional pictures for point by point assessment.
Treatment Alternatives for Spine Conditions
Treatment for spinal wounds shifts based on seriousness and sort but for the most part includes:
Traditionalist Treatments
Most spine conditions react well to non-surgical treatments:
Physical Treatment: Custom fitted works out to reinforce muscles and move forward flexibility.
Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for torment relief.
Injections: Corticosteroid infusions to diminish aggravation around nerves.
Surgical Treatments
In cases where preservationist medicines fall flat, surgery may be necessary:
Discectomy: Expulsion of herniated circle fabric to soothe nerve pressure.
Laminectomy: Evacuation of portion of the vertebra to calm weight on the spinal cord. Spinal
Combination: Joining two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine.
Preventive Measures for Spine Health
Maintaining spine wellbeing is pivotal for avoiding injuries:
Exercise Frequently: Lock in in exercises that fortify center muscles supporting the spine.
Maintain Great Pose: Utilize ergonomic furniture and be careful of pose whereas sitting or standing.
Lift Legitimately: Twist at the knees instep of at the midriff when lifting overwhelming objects.
Stay Hydrated: Satisfactory hydration makes a difference keep up circle health.
Comprehensive Guide to Spine Injuries and Conditions: Back and Neck Health Explained
Spine wounds and conditions can have significant impacts on day by day life. Understanding their causes, side effects, determination strategies, treatment alternatives, and preventive measures is basic for keeping up spine wellbeing. If you involvement determined back or neck torment, counsel a healthcare proficient for an precise determination and suitable administration plan.
By prioritizing spine wellbeing through mindfulness and preventive methodologies, people can improve their by and large well-being and diminish their hazard of harm.
Structure of the Spine: The human spine is composed of 33 vertebrae, which consolidate: 7 cervical vertebrae in the neck, 12 thoracic vertebrae in the upper back, 5 lumbar vertebrae in the lower back.
Additionally, there are melded vertebrae forming the sacrum and coccyx.
Intervertebral Circles:
Between each vertebra are intervertebral plates that act as cushions to absorb weight and maintain a strategic distance from bone-on-bone contact. This cushioning is essential for flexibility and advancement.
Capacities of the Spine: The spine serves a few fundamental capacities: It gives assistant back for the body. It guarantees the spinal line and nerve roots, It licenses for versatility and movement.
Ligaments and Muscles: The spine comprises different ligaments (around 220) and muscles (over 120), which contribute to its soundness and mobility.
Developmental Viewpoints: At birth, the spine comprises of 33 vertebrae, but a few combine together in the midst of advancement, driving to grown-ups commonly having 26 valuable vertebrae.
Spinal Canal: The spinal canal houses the spinal line, with its separate over moving over unmistakable districts of the spine, being greater in the cervical and lumbar ranges compared to the thoracic region.
The information you are looking for to confirm is without a question exact based on these strong sources. If you have specific points of view you’d like to jump more significant into or clarify development, feel free to ask.